ISL1 is an essential determinant of structural and functional tonotopic representation of sound | bioRxiv

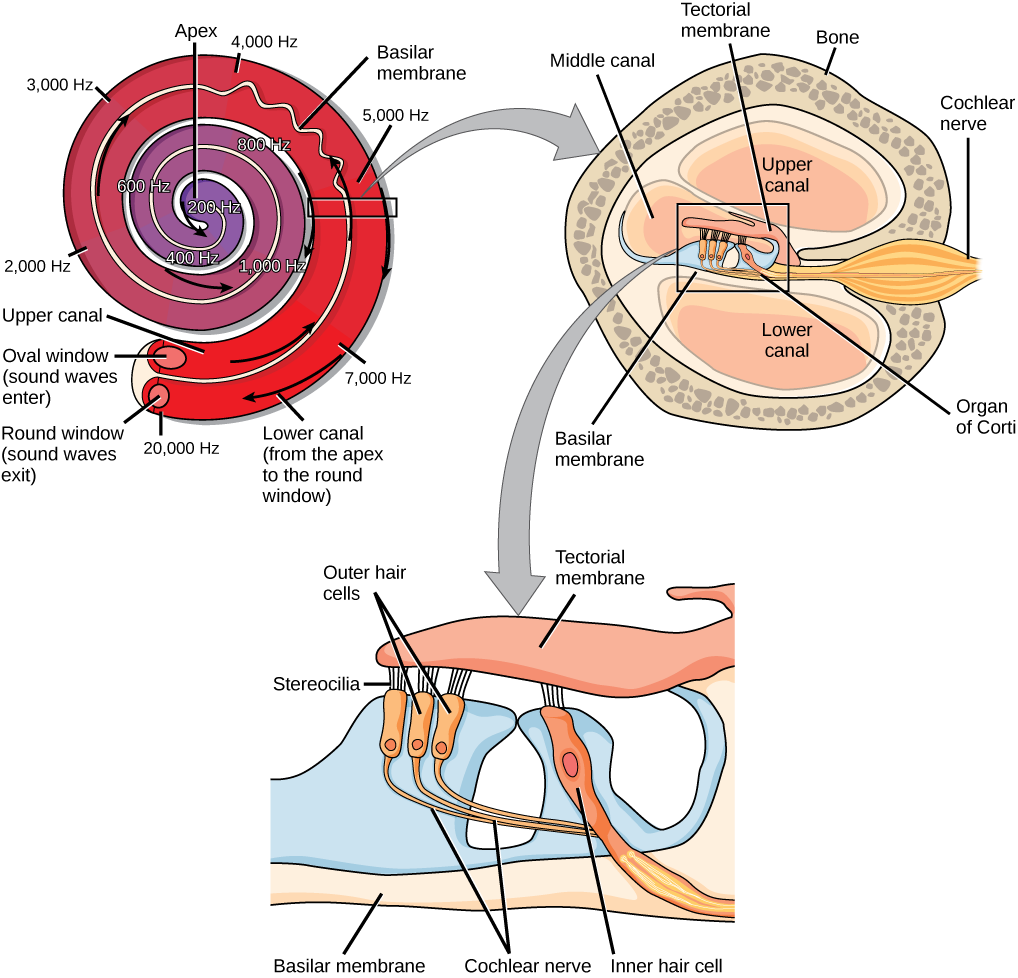
Encoding sound in the cochlea: from receptor potential to afferent discharge - Rutherford - 2021 - The Journal of Physiology - Wiley Online Library

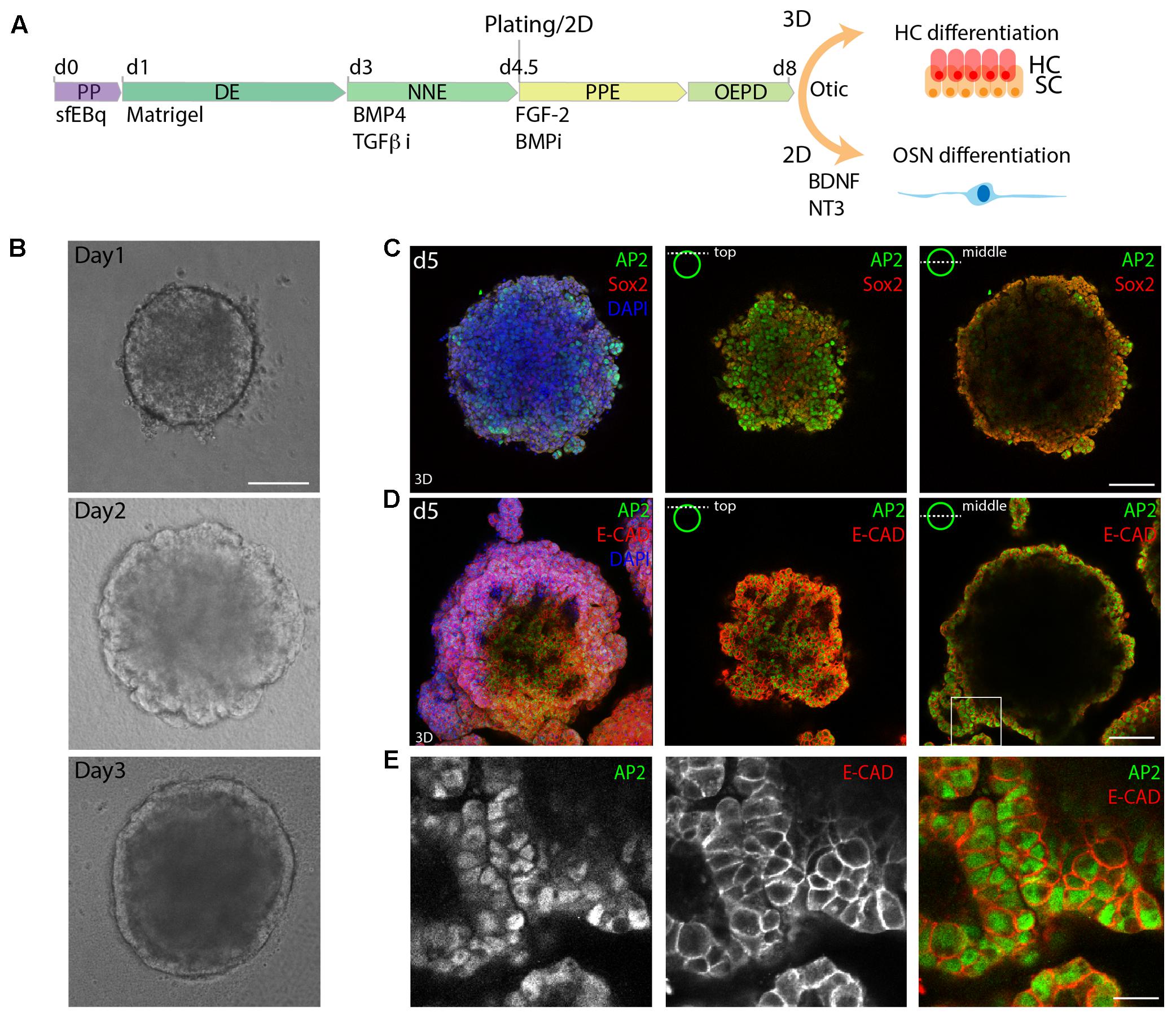
ISL1 is necessary for auditory neuron development and contributes toward tonotopic organization | PNAS

Neuronal processes and glial precursors form a scaffold for wiring the developing mouse cochlea | Nature Communications

Developmental Profiling of Spiral Ganglion Neurons Reveals Insights into Auditory Circuit Assembly | Journal of Neuroscience

Recent advances in the development and function of type II spiral ganglion neurons in the mammalian inner ear. | Semantic Scholar
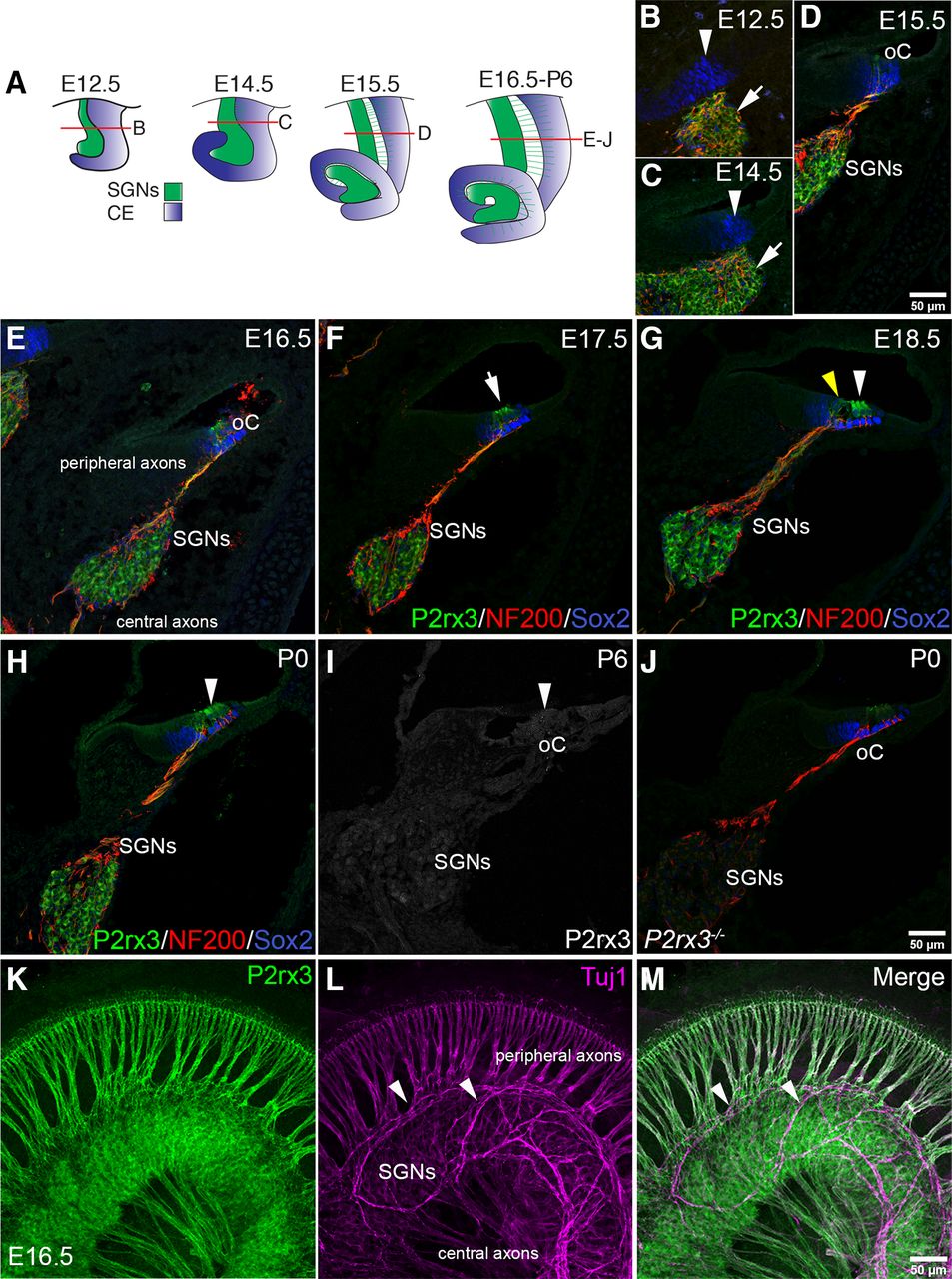
The Purinergic Receptor P2rx3 is Required for Spiral Ganglion Neuron Branch Refinement during Development | eNeuro
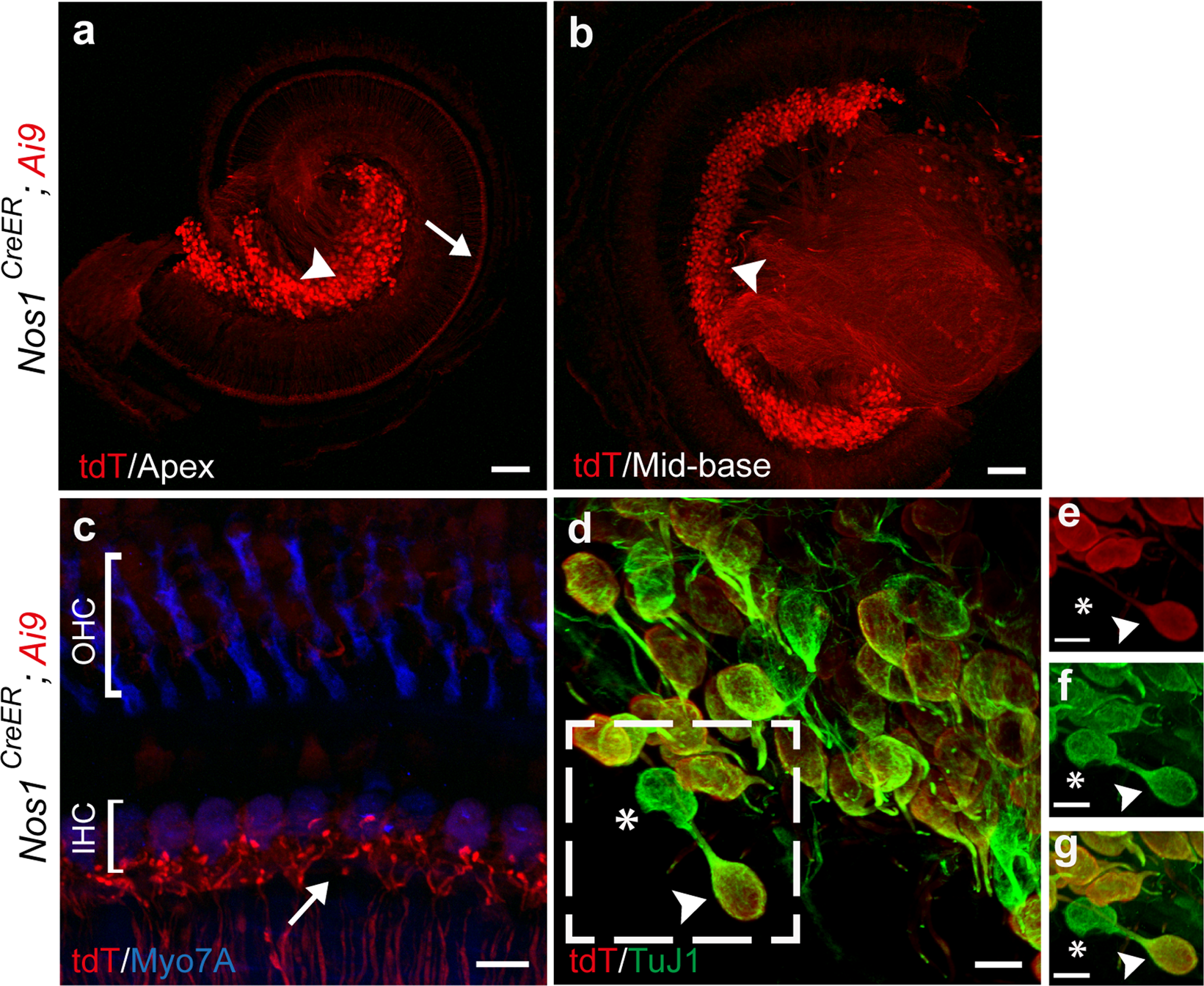
Characterization of transgenic mouse lines for labeling type I and type II afferent neurons in the cochlea | Scientific Reports

Recent advances in the development and function of type II spiral ganglion neurons in the mammalian inner ear - ScienceDirect

Frontiers | Single-Cell RNA Analysis of Type I Spiral Ganglion Neurons Reveals a Lmx1a Population in the Cochlea
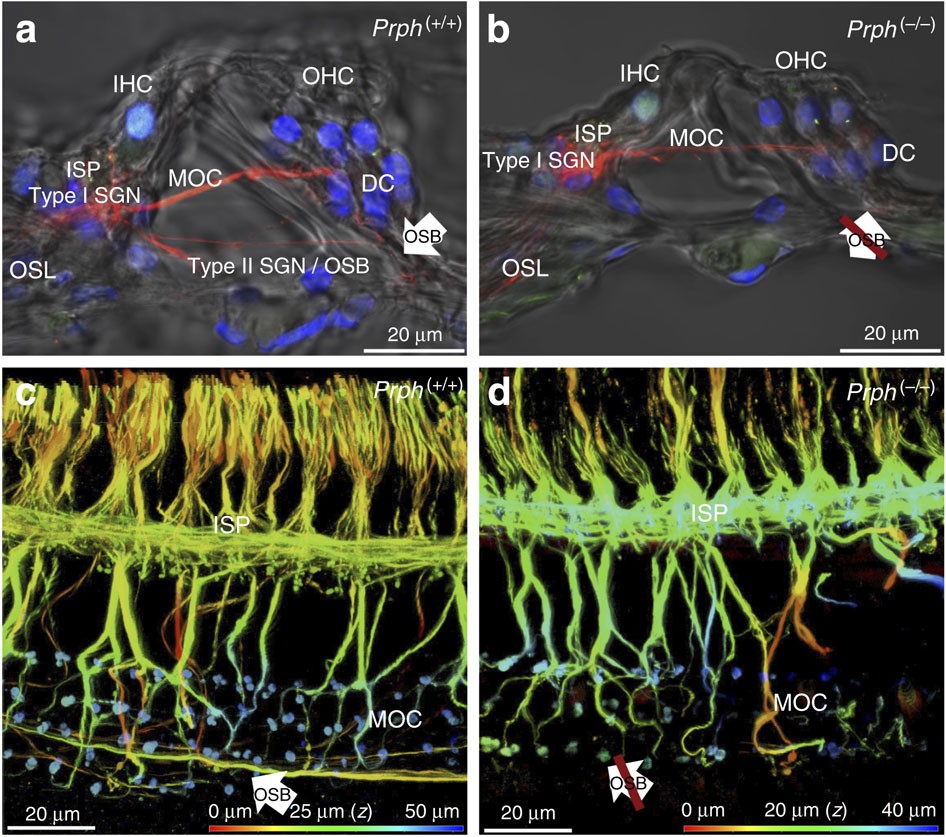
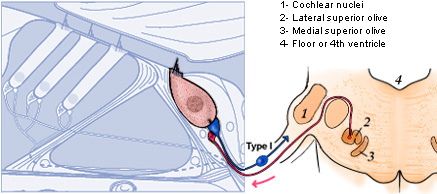
Type II spiral ganglion afferent neurons drive medial olivocochlear reflex suppression of the cochlear amplifier | Nature Communications
Altered expression of genes regulating inflammation and synaptogenesis during regrowth of afferent neurons to cochlear hair cells | PLOS ONE